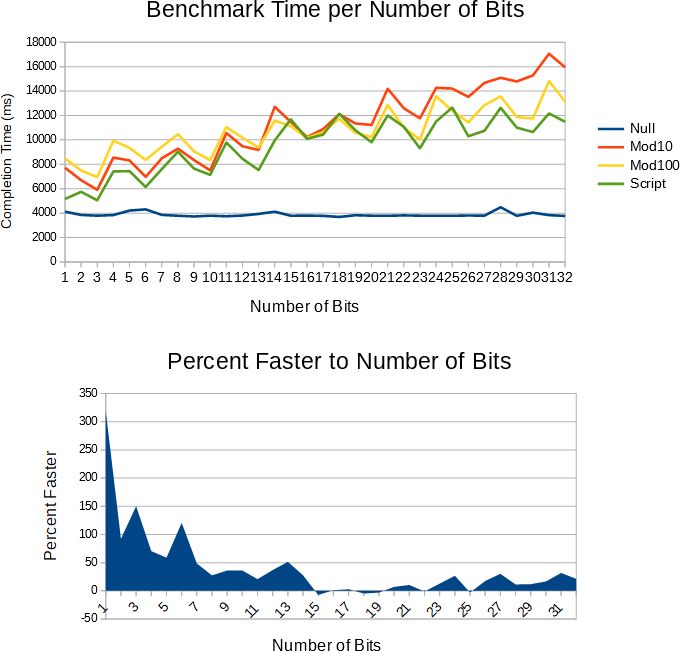
L'ho tenuto in giro per un po 'e finalmente sono riuscito a pubblicarlo.
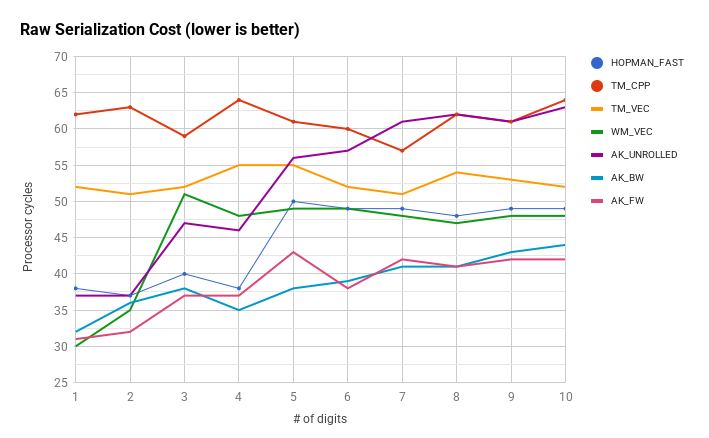
Qualche metodo in più rispetto alla doppia parola alla volta hopman_fast . I risultati si riferiscono allo std :: string ottimizzato per le stringhe brevi di GCC, altrimenti le differenze di prestazioni vengono oscurate dall'overhead del codice di gestione delle stringhe copy-on-write. La velocità effettiva viene misurata nello stesso modo in cui altrove in questo argomento, i conteggi dei cicli sono per le parti di serializzazione non elaborate del codice prima di copiare il buffer di output in una stringa.
HOPMAN_FAST - performance reference
TM_CPP, TM_VEC - scalar and vector versions of Terje Mathisen algorithm
WM_VEC - intrinsics implementation of Wojciech Mula's vector algorithm
AK_BW - word-at-a-time routine with a jump table that fills a buffer in reverse
AK_FW - forward-stepping word-at-a-time routine with a jump table in assembly
AK_UNROLLED - generic word-at-a-time routine that uses an unrolled loop

Interruttori del tempo di compilazione:
-DVSTRING - abilita le stringhe SSO per le configurazioni GCC meno
recenti -DBSR1 - abilita fast log10
-DRDTSC - abilita contatori di cicli
#include <cstdio>
#include <iostream>
#include <climits>
#include <sstream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <limits>
#include <ctime>
#include <stdint.h>
#include <x86intrin.h>
/* Uncomment to run */
// #define HOPMAN_FAST
// #define TM_CPP
// #define TM_VEC
// #define WM_VEC
// #define AK_UNROLLED
// #define AK_BW
// #define AK_FW
using namespace std;
#ifdef VSTRING
#include <ext/vstring.h>
typedef __gnu_cxx::__vstring string_type;
#else
typedef string string_type;
#endif
namespace detail {
#ifdef __GNUC__
#define ALIGN(N) __attribute__ ((aligned(N)))
#define PACK __attribute__ ((packed))
inline size_t num_digits(unsigned u) {
struct {
uint32_t count;
uint32_t max;
} static digits[32] ALIGN(64) = {
{ 1, 9 }, { 1, 9 }, { 1, 9 }, { 1, 9 },
{ 2, 99 }, { 2, 99 }, { 2, 99 },
{ 3, 999 }, { 3, 999 }, { 3, 999 },
{ 4, 9999 }, { 4, 9999 }, { 4, 9999 }, { 4, 9999 },
{ 5, 99999 }, { 5, 99999 }, { 5, 99999 },
{ 6, 999999 }, { 6, 999999 }, { 6, 999999 },
{ 7, 9999999 }, { 7, 9999999 }, { 7, 9999999 }, { 7, 9999999 },
{ 8, 99999999 }, { 8, 99999999 }, { 8, 99999999 },
{ 9, 999999999 }, { 9, 999999999 }, { 9, 999999999 },
{ 10, UINT_MAX }, { 10, UINT_MAX }
};
#if (defined(i386) || defined(__x86_64__)) && (defined(BSR1) || defined(BSR2))
size_t l = u;
#if defined(BSR1)
__asm__ __volatile__ (
"bsrl %k0, %k0 \n\t"
"shlq $32, %q1 \n\t"
"movq %c2(,%0,8), %0\n\t"
"cmpq %0, %q1 \n\t"
"seta %b1 \n\t"
"addl %1, %k0 \n\t"
: "+r" (l), "+r"(u)
: "i"(digits)
: "cc"
);
return l;
#else
__asm__ __volatile__ ( "bsr %0, %0;" : "+r" (l) );
return digits[l].count + ( u > digits[l].max );
#endif
#else
size_t l = (u != 0) ? 31 - __builtin_clz(u) : 0;
return digits[l].count + ( u > digits[l].max );
#endif
}
#else
inline unsigned msb_u32(unsigned x) {
static const unsigned bval[] = { 0,1,2,2,3,3,3,3,4,4,4,4,4,4,4,4 };
unsigned base = 0;
if (x & (unsigned) 0xFFFF0000) { base += 32/2; x >>= 32/2; }
if (x & (unsigned) 0x0000FF00) { base += 32/4; x >>= 32/4; }
if (x & (unsigned) 0x000000F0) { base += 32/8; x >>= 32/8; }
return base + bval[x];
}
inline size_t num_digits(unsigned x) {
static const unsigned powertable[] = {
0,10,100,1000,10000,100000,1000000,10000000,100000000, 1000000000 };
size_t lg_ten = msb_u32(x) * 1233 >> 12;
size_t adjust = (x >= powertable[lg_ten]);
return lg_ten + adjust;
}
#endif /* __GNUC__ */
struct CharBuffer {
class reverse_iterator : public iterator<random_access_iterator_tag, char> {
char* m_p;
public:
reverse_iterator(char* p) : m_p(p - 1) {}
reverse_iterator operator++() { return --m_p; }
reverse_iterator operator++(int) { return m_p--; }
char operator*() const { return *m_p; }
bool operator==( reverse_iterator it) const { return m_p == it.m_p; }
bool operator!=( reverse_iterator it) const { return m_p != it.m_p; }
difference_type operator-( reverse_iterator it) const { return it.m_p - m_p; }
};
};
union PairTable {
char c[2];
unsigned short u;
} PACK table[100] ALIGN(1024) = {
{{'0','0'}},{{'0','1'}},{{'0','2'}},{{'0','3'}},{{'0','4'}},{{'0','5'}},{{'0','6'}},{{'0','7'}},{{'0','8'}},{{'0','9'}},
{{'1','0'}},{{'1','1'}},{{'1','2'}},{{'1','3'}},{{'1','4'}},{{'1','5'}},{{'1','6'}},{{'1','7'}},{{'1','8'}},{{'1','9'}},
{{'2','0'}},{{'2','1'}},{{'2','2'}},{{'2','3'}},{{'2','4'}},{{'2','5'}},{{'2','6'}},{{'2','7'}},{{'2','8'}},{{'2','9'}},
{{'3','0'}},{{'3','1'}},{{'3','2'}},{{'3','3'}},{{'3','4'}},{{'3','5'}},{{'3','6'}},{{'3','7'}},{{'3','8'}},{{'3','9'}},
{{'4','0'}},{{'4','1'}},{{'4','2'}},{{'4','3'}},{{'4','4'}},{{'4','5'}},{{'4','6'}},{{'4','7'}},{{'4','8'}},{{'4','9'}},
{{'5','0'}},{{'5','1'}},{{'5','2'}},{{'5','3'}},{{'5','4'}},{{'5','5'}},{{'5','6'}},{{'5','7'}},{{'5','8'}},{{'5','9'}},
{{'6','0'}},{{'6','1'}},{{'6','2'}},{{'6','3'}},{{'6','4'}},{{'6','5'}},{{'6','6'}},{{'6','7'}},{{'6','8'}},{{'6','9'}},
{{'7','0'}},{{'7','1'}},{{'7','2'}},{{'7','3'}},{{'7','4'}},{{'7','5'}},{{'7','6'}},{{'7','7'}},{{'7','8'}},{{'7','9'}},
{{'8','0'}},{{'8','1'}},{{'8','2'}},{{'8','3'}},{{'8','4'}},{{'8','5'}},{{'8','6'}},{{'8','7'}},{{'8','8'}},{{'8','9'}},
{{'9','0'}},{{'9','1'}},{{'9','2'}},{{'9','3'}},{{'9','4'}},{{'9','5'}},{{'9','6'}},{{'9','7'}},{{'9','8'}},{{'9','9'}}
};
} // namespace detail
struct progress_timer {
clock_t c;
progress_timer() : c(clock()) {}
int elapsed() { return clock() - c; }
~progress_timer() {
clock_t d = clock() - c;
cout << d / CLOCKS_PER_SEC << "."
<< (((d * 1000) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC) % 1000 / 100)
<< (((d * 1000) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC) % 100 / 10)
<< (((d * 1000) / CLOCKS_PER_SEC) % 10)
<< " s" << endl;
}
};
#ifdef HOPMAN_FAST
namespace hopman_fast {
static unsigned long cpu_cycles = 0;
struct itostr_helper {
static ALIGN(1024) unsigned out[10000];
itostr_helper() {
for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
unsigned v = i;
char * o = (char*)(out + i);
o[3] = v % 10 + '0';
o[2] = (v % 100) / 10 + '0';
o[1] = (v % 1000) / 100 + '0';
o[0] = (v % 10000) / 1000;
if (o[0]) o[0] |= 0x30;
else if (o[1] != '0') o[0] |= 0x20;
else if (o[2] != '0') o[0] |= 0x10;
else o[0] |= 0x00;
}
}
};
unsigned itostr_helper::out[10000];
itostr_helper hlp_init;
template <typename T>
string_type itostr(T o) {
typedef itostr_helper hlp;
#ifdef RDTSC
long first_clock = __rdtsc();
#endif
unsigned blocks[3], *b = blocks + 2;
blocks[0] = o < 0 ? ~o + 1 : o;
blocks[2] = blocks[0] % 10000; blocks[0] /= 10000;
blocks[2] = hlp::out[blocks[2]];
if (blocks[0]) {
blocks[1] = blocks[0] % 10000; blocks[0] /= 10000;
blocks[1] = hlp::out[blocks[1]];
blocks[2] |= 0x30303030;
b--;
}
if (blocks[0]) {
blocks[0] = hlp::out[blocks[0] % 10000];
blocks[1] |= 0x30303030;
b--;
}
char* f = ((char*)b);
f += 3 - (*f >> 4);
char* str = (char*)blocks;
if (o < 0) *--f = '-';
str += 12;
#ifdef RDTSC
cpu_cycles += __rdtsc() - first_clock;
#endif
return string_type(f, str);
}
unsigned long cycles() { return cpu_cycles; }
void reset() { cpu_cycles = 0; }
}
#endif
namespace ak {
#ifdef AK_UNROLLED
namespace unrolled {
static unsigned long cpu_cycles = 0;
template <typename value_type> class Proxy {
static const size_t MaxValueSize = 16;
static inline char* generate(int value, char* buffer) {
union { char* pc; unsigned short* pu; } b = { buffer + MaxValueSize };
unsigned u, v = value < 0 ? unsigned(~value) + 1 : value;
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
if ((v /= 100)) {
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
if ((v /= 100)) {
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
if ((v /= 100)) {
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
if ((v /= 100)) {
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
} } } }
*(b.pc -= (u >= 10)) = '-';
return b.pc + (value >= 0);
}
static inline char* generate(unsigned value, char* buffer) {
union { char* pc; unsigned short* pu; } b = { buffer + MaxValueSize };
unsigned u, v = value;
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
if ((v /= 100)) {
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
if ((v /= 100)) {
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
if ((v /= 100)) {
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
if ((v /= 100)) {
*--b.pu = detail::table[v % 100].u; u = v;
} } } }
return b.pc + (u < 10);
}
public:
static inline string_type convert(value_type v) {
char buf[MaxValueSize];
#ifdef RDTSC
long first_clock = __rdtsc();
#endif
char* p = generate(v, buf);
char* e = buf + MaxValueSize;
#ifdef RDTSC
cpu_cycles += __rdtsc() - first_clock;
#endif
return string_type(p, e);
}
};
string_type itostr(int i) { return Proxy<int>::convert(i); }
string_type itostr(unsigned i) { return Proxy<unsigned>::convert(i); }
unsigned long cycles() { return cpu_cycles; }
void reset() { cpu_cycles = 0; }
}
#endif
#if defined(AK_BW)
namespace bw {
static unsigned long cpu_cycles = 0;
typedef uint64_t u_type;
template <typename value_type> class Proxy {
static inline void generate(unsigned v, size_t len, char* buffer) {
u_type u = v;
switch(len) {
default: u = (v * 1374389535ULL) >> 37; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + 8) = detail::table[v -= 100 * u].u;
case 8: v = (u * 1374389535ULL) >> 37; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + 6) = detail::table[u -= 100 * v].u;
case 6: u = (v * 1374389535ULL) >> 37; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + 4) = detail::table[v -= 100 * u].u;
case 4: v = (u * 167773) >> 24; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + 2) = detail::table[u -= 100 * v].u;
case 2: *(uint16_t*)buffer = detail::table[v].u;
case 0: return;
case 9: u = (v * 1374389535ULL) >> 37; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + 7) = detail::table[v -= 100 * u].u;
case 7: v = (u * 1374389535ULL) >> 37; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + 5) = detail::table[u -= 100 * v].u;
case 5: u = (v * 1374389535ULL) >> 37; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + 3) = detail::table[v -= 100 * u].u;
case 3: v = (u * 167773) >> 24; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + 1) = detail::table[u -= 100 * v].u;
case 1: *buffer = v + 0x30;
}
}
public:
static inline string_type convert(bool neg, unsigned val) {
char buf[16];
#ifdef RDTSC
long first_clock = __rdtsc();
#endif
size_t len = detail::num_digits(val);
buf[0] = '-';
char* e = buf + neg;
generate(val, len, e);
e += len;
#ifdef RDTSC
cpu_cycles += __rdtsc() - first_clock;
#endif
return string_type(buf, e);
}
};
string_type itostr(int i) { return Proxy<int>::convert(i < 0, i < 0 ? unsigned(~i) + 1 : i); }
string_type itostr(unsigned i) { return Proxy<unsigned>::convert(false, i); }
unsigned long cycles() { return cpu_cycles; }
void reset() { cpu_cycles = 0; }
}
#endif
#if defined(AK_FW)
namespace fw {
static unsigned long cpu_cycles = 0;
typedef uint32_t u_type;
template <typename value_type> class Proxy {
static inline void generate(unsigned v, size_t len, char* buffer) {
#if defined(__GNUC__) && defined(__x86_64__)
uint16_t w;
uint32_t u;
__asm__ __volatile__ (
"jmp %*T%=(,%3,8) \n\t"
"T%=: .quad L0%= \n\t"
" .quad L1%= \n\t"
" .quad L2%= \n\t"
" .quad L3%= \n\t"
" .quad L4%= \n\t"
" .quad L5%= \n\t"
" .quad L6%= \n\t"
" .quad L7%= \n\t"
" .quad L8%= \n\t"
" .quad L9%= \n\t"
" .quad L10%= \n\t"
"L10%=: \n\t"
" imulq $1441151881, %q0, %q1\n\t"
" shrq $57, %q1 \n\t"
" movw %c5(,%q1,2), %w2 \n\t"
" imull $100000000, %1, %1 \n\t"
" subl %1, %0 \n\t"
" movw %w2, (%4) \n\t"
"L8%=: \n\t"
" imulq $1125899907, %q0, %q1\n\t"
" shrq $50, %q1 \n\t"
" movw %c5(,%q1,2), %w2 \n\t"
" imull $1000000, %1, %1 \n\t"
" subl %1, %0 \n\t"
" movw %w2, -8(%4,%3) \n\t"
"L6%=: \n\t"
" imulq $429497, %q0, %q1 \n\t"
" shrq $32, %q1 \n\t"
" movw %c5(,%q1,2), %w2 \n\t"
" imull $10000, %1, %1 \n\t"
" subl %1, %0 \n\t"
" movw %w2, -6(%4,%3) \n\t"
"L4%=: \n\t"
" imull $167773, %0, %1 \n\t"
" shrl $24, %1 \n\t"
" movw %c5(,%q1,2), %w2 \n\t"
" imull $100, %1, %1 \n\t"
" subl %1, %0 \n\t"
" movw %w2, -4(%4,%3) \n\t"
"L2%=: \n\t"
" movw %c5(,%q0,2), %w2 \n\t"
" movw %w2, -2(%4,%3) \n\t"
"L0%=: jmp 1f \n\t"
"L9%=: \n\t"
" imulq $1801439851, %q0, %q1\n\t"
" shrq $54, %q1 \n\t"
" movw %c5(,%q1,2), %w2 \n\t"
" imull $10000000, %1, %1 \n\t"
" subl %1, %0 \n\t"
" movw %w2, (%4) \n\t"
"L7%=: \n\t"
" imulq $43980466, %q0, %q1 \n\t"
" shrq $42, %q1 \n\t"
" movw %c5(,%q1,2), %w2 \n\t"
" imull $100000, %1, %1 \n\t"
" subl %1, %0 \n\t"
" movw %w2, -7(%4,%3) \n\t"
"L5%=: \n\t"
" imulq $268436, %q0, %q1 \n\t"
" shrq $28, %q1 \n\t"
" movw %c5(,%q1,2), %w2 \n\t"
" imull $1000, %1, %1 \n\t"
" subl %1, %0 \n\t"
" movw %w2, -5(%4,%3) \n\t"
"L3%=: \n\t"
" imull $6554, %0, %1 \n\t"
" shrl $15, %1 \n\t"
" andb $254, %b1 \n\t"
" movw %c5(,%q1), %w2 \n\t"
" leal (%1,%1,4), %1 \n\t"
" subl %1, %0 \n\t"
" movw %w2, -3(%4,%3) \n\t"
"L1%=: \n\t"
" addl $48, %0 \n\t"
" movb %b0, -1(%4,%3) \n\t"
"1: \n\t"
: "+r"(v), "=&q"(u), "=&r"(w)
: "r"(len), "r"(buffer), "i"(detail::table)
: "memory", "cc"
);
#else
u_type u;
switch(len) {
default: u = (v * 1441151881ULL) >> 57; *(uint16_t*)(buffer) = detail::table[u].u; v -= u * 100000000;
case 8: u = (v * 1125899907ULL) >> 50; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + len - 8) = detail::table[u].u; v -= u * 1000000;
case 6: u = (v * 429497ULL) >> 32; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + len - 6) = detail::table[u].u; v -= u * 10000;
case 4: u = (v * 167773) >> 24; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + len - 4) = detail::table[u].u; v -= u * 100;
case 2: *(uint16_t*)(buffer + len - 2) = detail::table[v].u;
case 0: return;
case 9: u = (v * 1801439851ULL) >> 54; *(uint16_t*)(buffer) = detail::table[u].u; v -= u * 10000000;
case 7: u = (v * 43980466ULL) >> 42; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + len - 7) = detail::table[u].u; v -= u * 100000;
case 5: u = (v * 268436ULL) >> 28; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + len - 5) = detail::table[u].u; v -= u * 1000;
case 3: u = (v * 6554) >> 16; *(uint16_t*)(buffer + len - 3) = detail::table[u].u; v -= u * 10;
case 1: *(buffer + len - 1) = v + 0x30;
}
#endif
}
public:
static inline string_type convert(bool neg, unsigned val) {
char buf[16];
#ifdef RDTSC
long first_clock = __rdtsc();
#endif
size_t len = detail::num_digits(val);
if (neg) buf[0] = '-';
char* e = buf + len + neg;
generate(val, len, buf + neg);
#ifdef RDTSC
cpu_cycles += __rdtsc() - first_clock;
#endif
return string_type(buf, e);
}
};
string_type itostr(int i) { return Proxy<int>::convert(i < 0, i < 0 ? unsigned(~i) + 1 : i); }
string_type itostr(unsigned i) { return Proxy<unsigned>::convert(false, i); }
unsigned long cycles() { return cpu_cycles; }
void reset() { cpu_cycles = 0; }
}
#endif
} // ak
namespace wm {
#ifdef WM_VEC
#if defined(__GNUC__) && defined(__x86_64__)
namespace vec {
static unsigned long cpu_cycles = 0;
template <typename value_type> class Proxy {
static inline unsigned generate(unsigned v, char* buf) {
static struct {
unsigned short mul_10[8];
unsigned short div_const[8];
unsigned short shl_const[8];
unsigned char to_ascii[16];
} ALIGN(64) bits =
{
{ // mul_10
10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10, 10
},
{ // div_const
8389, 5243, 13108, 0x8000, 8389, 5243, 13108, 0x8000
},
{ // shl_const
1 << (16 - (23 + 2 - 16)),
1 << (16 - (19 + 2 - 16)),
1 << (16 - 1 - 2),
1 << (15),
1 << (16 - (23 + 2 - 16)),
1 << (16 - (19 + 2 - 16)),
1 << (16 - 1 - 2),
1 << (15)
},
{ // to_ascii
'0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0',
'0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0', '0'
}
};
unsigned x, y, l;
x = (v * 1374389535ULL) >> 37;
y = v;
l = 0;
if (x) {
unsigned div = 0xd1b71759;
unsigned mul = 55536;
__m128i z, m, a, o;
y -= 100 * x;
z = _mm_cvtsi32_si128(x);
m = _mm_load_si128((__m128i*)bits.mul_10);
o = _mm_mul_epu32( z, _mm_cvtsi32_si128(div));
z = _mm_add_epi32( z, _mm_mul_epu32( _mm_cvtsi32_si128(mul), _mm_srli_epi64( o, 45) ) );
z = _mm_slli_epi64( _mm_shuffle_epi32( _mm_unpacklo_epi16(z, z), 5 ), 2 );
a = _mm_load_si128((__m128i*)bits.to_ascii);
z = _mm_mulhi_epu16( _mm_mulhi_epu16( z, *(__m128i*)bits.div_const ), *(__m128i*)bits.shl_const );
z = _mm_sub_epi16( z, _mm_slli_epi64( _mm_mullo_epi16( m, z ), 16 ) );
z = _mm_add_epi8( _mm_packus_epi16( z, _mm_xor_si128(o, o) ), a );
x = __builtin_ctz( ~_mm_movemask_epi8( _mm_cmpeq_epi8( a, z ) ) );
l = 8 - x;
uint64_t q = _mm_cvtsi128_si64(z) >> (x * 8);
*(uint64_t*)buf = q;
buf += l;
x = 1;
}
v = (y * 6554) >> 16;
l += 1 + (x | (v != 0));
*(unsigned short*)buf = 0x30 + ((l > 1) ? ((0x30 + y - v * 10) << 8) + v : y);
return l;
}
public:
static inline string_type convert(bool neg, unsigned val) {
char buf[16];
#ifdef RDTSC
long first_clock = __rdtsc();
#endif
buf[0] = '-';
unsigned len = generate(val, buf + neg);
char* e = buf + len + neg;
#ifdef RDTSC
cpu_cycles += __rdtsc() - first_clock;
#endif
return string_type(buf, e);
}
};
inline string_type itostr(int i) { return Proxy<int>::convert(i < 0, i < 0 ? unsigned(~i) + 1 : i); }
inline string_type itostr(unsigned i) { return Proxy<unsigned>::convert(false, i); }
unsigned long cycles() { return cpu_cycles; }
void reset() { cpu_cycles = 0; }
}
#endif
#endif
} // wm
namespace tmn {
#ifdef TM_CPP
namespace cpp {
static unsigned long cpu_cycles = 0;
template <typename value_type> class Proxy {
static inline void generate(unsigned v, char* buffer) {
unsigned const f1_10000 = (1 << 28) / 10000;
unsigned tmplo, tmphi;
unsigned lo = v % 100000;
unsigned hi = v / 100000;
tmplo = lo * (f1_10000 + 1) - (lo >> 2);
tmphi = hi * (f1_10000 + 1) - (hi >> 2);
unsigned mask = 0x0fffffff;
unsigned shift = 28;
for(size_t i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
buffer[i + 0] = '0' + (char)(tmphi >> shift);
buffer[i + 5] = '0' + (char)(tmplo >> shift);
tmphi = (tmphi & mask) * 5;
tmplo = (tmplo & mask) * 5;
mask >>= 1;
shift--;
}
}
public:
static inline string_type convert(bool neg, unsigned val) {
#ifdef RDTSC
long first_clock = __rdtsc();
#endif
char buf[16];
size_t len = detail::num_digits(val);
char* e = buf + 11;
generate(val, buf + 1);
buf[10 - len] = '-';
len += neg;
char* b = e - len;
#ifdef RDTSC
cpu_cycles += __rdtsc() - first_clock;
#endif
return string_type(b, e);
}
};
string_type itostr(int i) { return Proxy<int>::convert(i < 0, i < 0 ? unsigned(~i) + 1 : i); }
string_type itostr(unsigned i) { return Proxy<unsigned>::convert(false, i); }
unsigned long cycles() { return cpu_cycles; }
void reset() { cpu_cycles = 0; }
}
#endif
#ifdef TM_VEC
namespace vec {
static unsigned long cpu_cycles = 0;
template <typename value_type> class Proxy {
static inline unsigned generate(unsigned val, char* buffer) {
static struct {
unsigned char mul_10[16];
unsigned char to_ascii[16];
unsigned char gather[16];
unsigned char shift[16];
} ALIGN(64) bits = {
{ 10,0,0,0,10,0,0,0,10,0,0,0,10,0,0,0 },
{ '0','0','0','0','0','0','0','0','0','0','0','0','0','0','0','0' },
{ 3,5,6,7,9,10,11,13,14,15,0,0,0,0,0,0 },
{ 0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15 }
};
unsigned u = val / 1000000;
unsigned l = val - u * 1000000;
__m128i x, h, f, m, n;
n = _mm_load_si128((__m128i*)bits.mul_10);
x = _mm_set_epi64x( l, u );
h = _mm_mul_epu32( x, _mm_set1_epi32(4294968) );
x = _mm_sub_epi64( x, _mm_srli_epi64( _mm_mullo_epi32( h, _mm_set1_epi32(1000) ), 32 ) );
f = _mm_set1_epi32((1 << 28) / 1000 + 1);
m = _mm_srli_epi32( _mm_cmpeq_epi32(m, m), 4 );
x = _mm_shuffle_epi32( _mm_blend_epi16( x, h, 204 ), 177 );
f = _mm_sub_epi32( _mm_mullo_epi32(f, x), _mm_srli_epi32(x, 2) );
h = _mm_load_si128((__m128i*)bits.to_ascii);
x = _mm_srli_epi32(f, 28);
f = _mm_mullo_epi32( _mm_and_si128( f, m ), n );
x = _mm_or_si128( x, _mm_slli_epi32(_mm_srli_epi32(f, 28), 8) );
f = _mm_mullo_epi32( _mm_and_si128( f, m ), n );
x = _mm_or_si128( x, _mm_slli_epi32(_mm_srli_epi32(f, 28), 16) );
f = _mm_mullo_epi32( _mm_and_si128( f, m ), n );
x = _mm_or_si128( x, _mm_slli_epi32(_mm_srli_epi32(f, 28), 24) );
x = _mm_add_epi8( _mm_shuffle_epi8(x, *(__m128i*)bits.gather), h );
l = __builtin_ctz( ~_mm_movemask_epi8( _mm_cmpeq_epi8( h, x ) ) | (1 << 9) );
x = _mm_shuffle_epi8( x, _mm_add_epi8(*(__m128i*)bits.shift, _mm_set1_epi8(l) ) );
_mm_store_si128( (__m128i*)buffer, x );
return 10 - l;
}
public:
static inline string_type convert(bool neg, unsigned val) {
#ifdef RDTSC
long first_clock = __rdtsc();
#endif
char arena[32];
char* buf = (char*)((uintptr_t)(arena + 16) & ~(uintptr_t)0xf);
*(buf - 1)= '-';
unsigned len = generate(val, buf) + neg;
buf -= neg;
char* end = buf + len;
#ifdef RDTSC
cpu_cycles += __rdtsc() - first_clock;
#endif
return string_type(buf, end);
}
};
string_type itostr(int i) { return Proxy<int>::convert(i < 0, i < 0 ? unsigned(~i) + 1 : i); }
string_type itostr(unsigned i) { return Proxy<unsigned>::convert(false, i); }
unsigned long cycles() { return cpu_cycles; }
void reset() { cpu_cycles = 0; }
}
#endif
}
bool fail(string in, string_type out) {
cout << "failure: " << in << " => " << out << endl;
return false;
}
#define TEST(x, n) \
stringstream ss; \
string_type s = n::itostr(x); \
ss << (long long)x; \
if (::strcmp(ss.str().c_str(), s.c_str())) { \
passed = fail(ss.str(), s); \
break; \
}
#define test(x) { \
passed = true; \
if (0 && passed) { \
char c = CHAR_MIN; \
do { \
TEST(c, x); \
} while (c++ != CHAR_MAX); \
if (!passed) cout << #x << " failed char!!!" << endl; \
} \
if (0 && passed) { \
short c = numeric_limits<short>::min(); \
do { \
TEST(c, x); \
} while (c++ != numeric_limits<short>::max()); \
if (!passed) cout << #x << " failed short!!!" << endl; \
} \
if (passed) { \
int c = numeric_limits<int>::min(); \
do { \
TEST(c, x); \
} while ((c += 100000) < numeric_limits<int>::max() - 100000); \
if (!passed) cout << #x << " failed int!!!" << endl; \
} \
if (passed) { \
unsigned c = numeric_limits<unsigned>::max(); \
do { \
TEST(c, x); \
} while ((c -= 100000) > 100000); \
if (!passed) cout << #x << " failed unsigned int!!!" << endl; \
} \
}
#define time(x, N) \
if (passed) { \
static const int64_t limits[] = \
{0, 10, 100, 1000, 10000, 100000, \
1000000, 10000000, 100000000, 1000000000, 10000000000ULL }; \
long passes = 0; \
cout << #x << ": "; \
progress_timer t; \
uint64_t s = 0; \
if (do_time) { \
for (int n = 0; n < N1; n++) { \
int i = 0; \
while (i < N2) { \
int v = ((NM - i) % limits[N]) | (limits[N] / 10); \
int w = x::itostr(v).size() + \
x::itostr(-v).size(); \
i += w * mult; \
passes++; \
} \
s += i / mult; \
} \
} \
k += s; \
cout << N << " digits: " \
<< s / double(t.elapsed()) * CLOCKS_PER_SEC/1000000 << " MB/sec, " << (x::cycles() / passes >> 1) << " clocks per pass "; \
x::reset(); \
}
#define series(n) \
{ if (do_test) test(n); if (do_time) time(n, 1); if (do_time) time(n, 2); \
if (do_time) time(n, 3); if (do_time) time(n, 4); if (do_time) time(n, 5); \
if (do_time) time(n, 6); if (do_time) time(n, 7); if (do_time) time(n, 8); \
if (do_time) time(n, 9); if (do_time) time(n, 10); }
int N1 = 1, N2 = 500000000, NM = INT_MAX;
int mult = 1; // used to stay under timelimit on ideone
unsigned long long k = 0;
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
bool do_time = 1, do_test = 1;
bool passed = true;
#ifdef HOPMAN_FAST
series(hopman_fast)
#endif
#ifdef WM_VEC
series(wm::vec)
#endif
#ifdef TM_CPP
series(tmn::cpp)
#endif
#ifdef TM_VEC
series(tmn::vec)
#endif
#ifdef AK_UNROLLED
series(ak::unrolled)
#endif
#if defined(AK_BW)
series(ak::bw)
#endif
#if defined(AK_FW)
series(ak::fw)
#endif
return k;
}